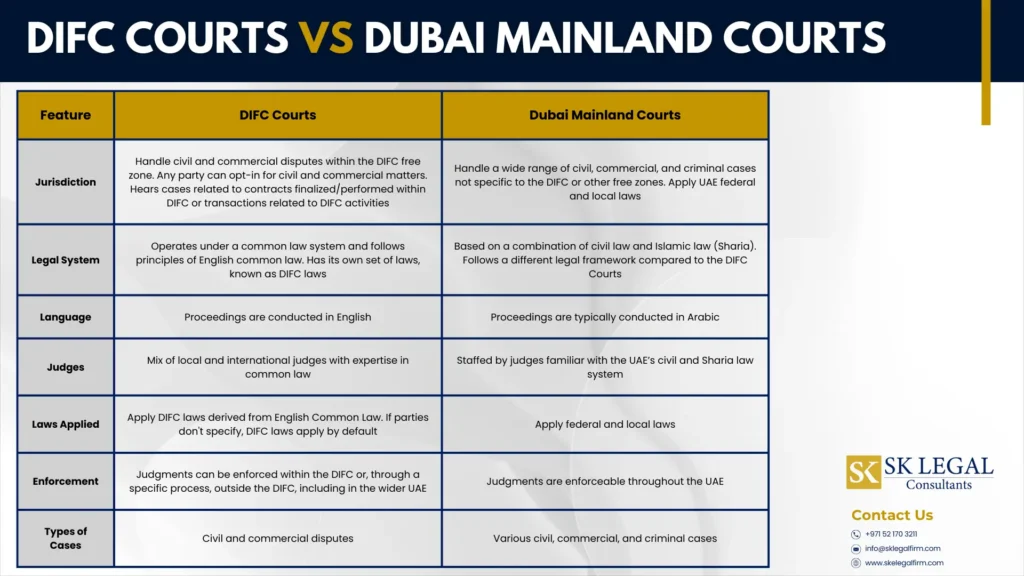
The Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) is a specialized financial free zone that operates under its own unique DIFC legal framework. DIFC has its own independent court system, which is known as DIFC Courts. These courts are governed by their own set of laws and regulations, separate from those applicable to other courts in Dubai or the UAE judicial system.
The DIFC Courts carry out their functions in an independent manner, in accordance with the provisions of the DIFC laws and regulations. The proceedings in DIFC take place in English language, unlike other Dubai mainland courts whose official language is Arabic.
DIFC Courts are renowned for their efficiency in managing commercial conflicts. The judges presiding over these courts possess specialized knowledge and expertise in commercial law. It equips them to make informed and effective decisions on complex disputes and cross-border legal disputes.
This specialized focus enhances the quality of justice delivered and instils confidence in businesses that their legal matters will be handled with the utmost professionalism and understanding of industry nuances.
DIFC Courts in Historical Context
The establishment of DIFC Courts was driven by a need for an autonomous judiciary specifically designed to cater to the requirements of the financial and commercial sectors. The specialized DIFC courts were established to provide a robust platform for dispute resolution, thereby enhancing confidence in the UAE legal system.
When Were the DIFC Courts Established?
The DIFC Courts were established under two laws enacted by the late Ruler of Dubai, His Highness Sheikh Maktoum bin Rashid Al Maktoum.
- Dubai Law No. 12 of 2004 (as amended by Dubai Law No. 16 of 2011 established the DIFC Courts, describes the jurisdiction of the Courts and provides for the independent administration of justice in the DIFC.
- DIFC Law No. 10 of 2004 sets out the powers, procedures, functions and administration of the DIFC Courts.
The laws establishing the DIFC Courts were designed to ensure the highest international standards of legal procedure, thus ensuring that the DIFC Courts provide the certainty, flexibility and efficiency expected by global institutions.
DIFC Court Structure and Jurisdiction
DIFC Courts consist of the Court of First Instance, Court of Appeal, and Small Claims Tribunal.
Court of First Instance
The Court of First Instance has exclusive jurisdiction to hear and determine civil and commercial cases wherein the parties opt into the jurisdiction of DIFC Courts in the contract, where the dispute involves a DIFC-established party, or if the dispute has occurred in DIFC.
The Court of Appeal
The Court of Appeal has exclusive jurisdiction to hear and determine appeals filed against Judgments or decisions made by the Court of First Instance as well as requests for interpretation of DIFC laws and regulations made by any of the DIFC’s bodies or establishments.
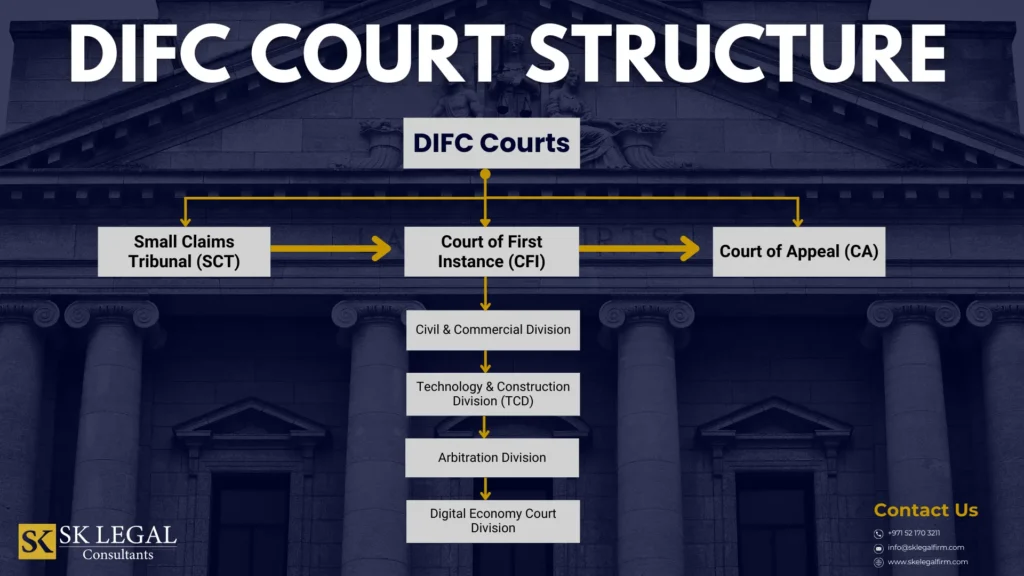
DIFC Small Claims Tribunal
The DIFC Small Claims Tribunal has jurisdiction to hear and determine civil and commercial disputes within the jurisdiction of the DIFC Courts in the following cases:
(i) If the value of the claim does not exceed AED 500,000
(ii) If the value of the claim exceeds the aforementioned amount but is less than AED 1,000,000 and for which the parties elected in writing that the SCT would hear it
(iii) If the claim relates to employment or former employment and for which the parties elected in writing, the SCT would hear it.
Technology and Construction Division (TCD)
Apart from the above, DIFC has a Technology and Construction Division (TCD). It is a specialist division that deals with technically complex claims, such as:
- complicated engineering disputes or claims arising out of fires,
- technology-related cases, such as liability for cybercrime incidents,
- disputes over the ownership and use of data,
- issues relating to emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence or connected cars.
Types of Cases Handled in DIFC Courts
The DIFC Courts have jurisdiction over civil and commercial disputes involving the DIFC or its entities and cases where the parties agree in writing to file such claim or action with the DIFC Courts (whether before or after the dispute arises).
The DIFC Courts handle various contractual and corporate matters, including those related to breach of contract, corporate governance, commercial disputes in Dubai, shareholder disputes, and other business-related conflicts.
The DIFC Courts also handle UAE contract law and employment-related issues such as wrongful termination, discrimination, breach of employment contract, unpaid wages, etc.
Application of Common Law Principles within DIFC Courts
The DIFC Courts function within a common law framework. It is separate from the civil law system that dominates the broader UAE legal landscape. This distinctive legal setting enables the DIFC to implement common law principles effectively.
DIFC has recently announced the enactment of key amendments to the Law on the Application of Civil and Commercial Laws in the DIFC (DIFC Law no. 3 of 2004). The purpose of these amendments is to provide clear statutory guidance regarding the sources and interpretation of DIFC Law, confirming that the DIFC statutes are supplemented by English common law as well as the common law of other jurisdictions.
The amendments confirm that DIFC Law is primarily determined by reference to DIFC statutes and the Judgments of the DIFC Courts that interpret and apply these statutes.
Furthermore, since DIFC Law is not designed to be strictly statutory, the amendments specify that it is supplemented by common law principles (including the principles and rules of equity). In interpreting common law for the DIFC, the Courts may refer to the common law of England and Wales as well as other common law jurisdictions.

Key Milestones and Achievements
The DIFC Courts exemplify a progressive approach towards integrating technology within the judicial system. Here are some key initiatives taken by the DIFC Courts:
1. E-filing Systems
The DIFC Courts have an e-filing system that facilitates the electronic submission of legal documents and claims. Users can submit various legal documents, including bundles, directly through the DIFC Courts’ portal without needing to visit the court physically. The e-filing system helps in streamlining the court processes and enables judges, lawyers, and court staff to access case information through the portal.
2. Virtual Hearings
Virtual hearings have become increasingly prevalent in DIFC Courts. In 2023, the DIFC Courts issued a Virtual Hearing and Bundling Protocol to standardize virtual court proceedings. The Protocol applies to civil and commercial proceedings conducted as Virtual Hearings under the jurisdiction of the Small Claims Tribunal, the Court of First Instance and the Court of Appeal.
3. Digital Economy Court
In 2021, the DIFC Courts established the Digital Economy Court Division to oversee sophisticated national and transnational disputes related to current and emerging technologies across areas ranging from big data, blockchain, AI, fintech, and cloud services to disputes also involving Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), 3D printing, and robotics.
4. AI Guidelines
The DIFC Courts have issued guidelines for incorporating AI in legal proceedings, highlighting the importance of transparency and responsible usage of AI-generated content in litigation. This initiative represents a crucial advancement in the integration of AI within legal practices while also addressing potential challenges.
5. Digital Assets Will
DIFC Courts recently announced the launch of a new suite of digital public services, including the Digital Assets Will. The Digital Assets Will empowers individuals to distribute their digital assets using a non-custodial DIFC Courts wallet.
A non-custodial wallet also allows an individual the freedom to reallocate the assets to the desired beneficiaries within their wallet, and for full control to mobilise in and out of the wallet in their lifetime, with assets finally distributed as ‘specific gifts’.
Get Expert Legal Advice on DIFC Courts with SK Legal
DIFC Courts are pivotal to the UAE’s legal and business landscape. It offers a robust platform for resolving commercial and financial disputes. At SK Legal, we offer expert legal guidance on handling the complexities of DIFC Courts. Our services include:
- Comprehensive Legal Consultancy: Personalised legal advice on cases within DIFC jurisdiction.
- Efficient Policy Review and Implementation: Assistance with DIFC contracts, DIFC litigation process, DIFC commercial arbitration, policies, and procedures.
- Specialised Legal Support: Experienced representation in all aspects of DIFC Courts, from litigation to arbitration.
For personalised assistance and expert legal advice on DIFC Courts, contact us at [email protected]
Disclaimer
This publication does not provide any legal advice and it is for information purposes only. You should not rely upon the material or information in this publication as a basis for making any business, legal or other decisions. Therefore, any reliance on such material is strictly at your own risk.
Share This Post On:
Learn More
Related Posts

February 14, 2025
Key Features of the DIFC Courts Legal Framework
Read more

January 29, 2025
How Corporate Law Firms Simplify Transactions For Businesses
Read more

December 16, 2024
Construction Contract in UAE: Legal Considerations For Foreign Developers…
CONTRIBUTOR

Sameer Khan is one of the Best Legal Consultants in UAE, and Founder and Managing Partner of SK Legal. He has been based in UAE for the past 14 years. During this time, he has successfully provided legal services to several prominent companies and private clients and has advised and represented them on a variety of projects in the UAE.
View all posts


